
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Share
Best Supplements for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints, which can lead to a reduced quality of life for those who suffer from it. Fortunately, there are natural supplements that can help manage the symptoms of RA and provide effective relief.
In this article, we will explore the top supplements that can help alleviate the effects of RA. Before delving into the list, it is important to understand RA and its effects, as well as the benefits of natural supplements for its management.
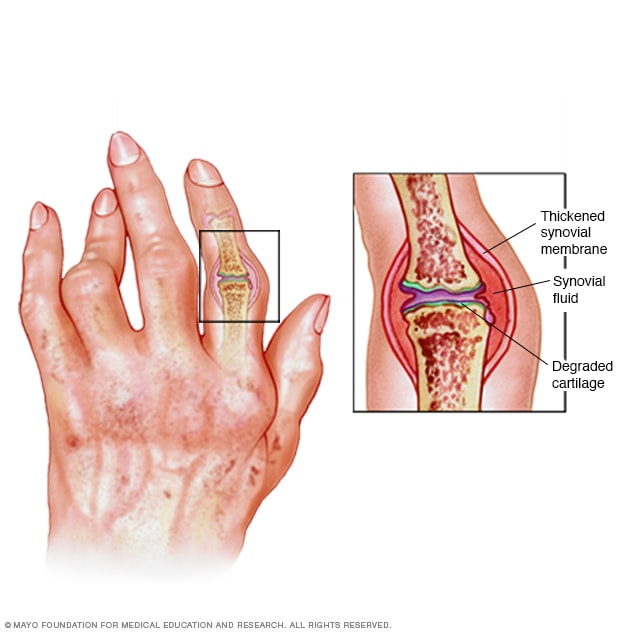
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In addition to joint involvement, RA can also affect other organs and systems in the body, such as the eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels (Fitzpatrick et al. 2005). The exact cause of RA is not fully understood, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors (Fitzpatrick et al. 2005).
The disease typically affects women more than men, and it can develop at any age, although the peak onset is between the ages of 30 and 50 years old (Fitzpatrick et al. 2005). The impact of RA on a person's life can be significant, as it can lead to chronic pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. It can also result in increased healthcare costs and a higher risk of comorbidities, such as depression and cardiovascular disease (Fitzpatrick et al. 2005).
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, stiffness, and potentially joint deformity. |
| Prevalence | Approximately 1% of the world population is affected by RA, with women being more commonly affected than men. |
| Onset | RA usually begins between the ages of 30 and 60, but it can occur at any age, including childhood (juvenile rheumatoid arthritis). |
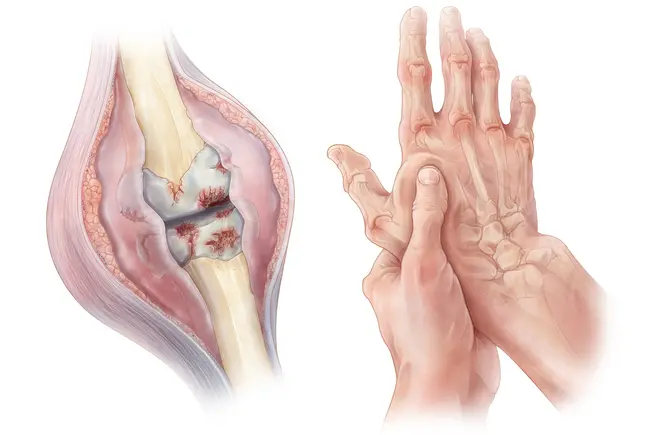
| Joint Involvement | RA typically affects the small joints of the hands and feet symmetrically, but it can also affect larger joints, such as the knees, hips, shoulders, and wrists. |
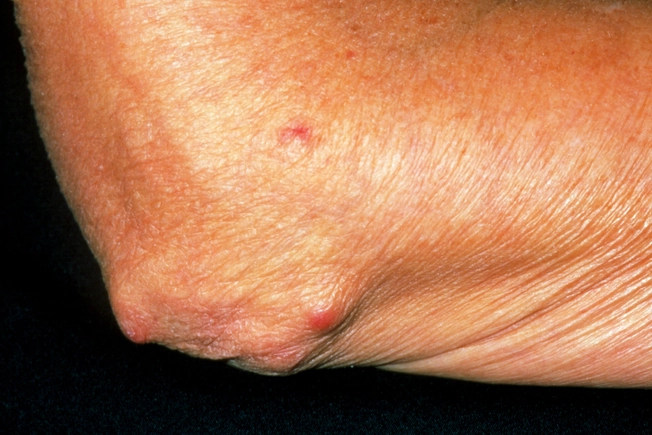
| Joint Symptoms | Common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, warmth, redness, and stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity. Joint deformities can develop. |
| Systemic Manifestations | RA can also involve other organs and systems, leading to fatigue, low-grade fever, loss of appetite, weight loss, and inflammation in the eyes, lungs, or blood vessels. |
| Progression | RA is a progressive disease with periods of remission and flare-ups. Over time, it can cause joint destruction, deformity, and loss of function. |
| Autoimmune Nature | The immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues, specifically the synovium (lining of the joints), leading to inflammation and joint damage. |
| Diagnostic Criteria | Diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, physical examination findings, blood tests (rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide), and imaging studies (X-rays, ultrasounds). |
| Treatment | Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, relieve symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. It may include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. |
| Prognosis | The prognosis varies, but early diagnosis and aggressive treatment can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve long-term outcomes. |
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing RA and preventing long-term damage to the joints and other organs. Treatment options include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise (Fitzpatrick et al. 2005). In conclusion, RA is a complex and debilitating disease that can have a significant impact on a person's life. Understanding the disease and its effects is essential in improving diagnosis, treatment, and management of this chronic condition.
Check the supplements we recommend for this conditions:
103. DrSous.Ca Bee Pearl pollen nectar enzyme blend 30 capsules
104. DrSous.Ca Bee Pearl Powder smoothie propolis royal jelly
142. DrSous.Ca Platinum Turmeric 60 Capsule Bottle
150. DrSous.Ca Turmeric Gummies high in antioxidants helps fight inflamation good for joint and skin
108. DRSOUS.CA Birch Chaga Truffles
107. DRSOUS.CA Birch Chaga Microbiome Wellness Powder
106. DrSous.Ca Birch Chaga Microbiome Wellness 30 Capsules
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the joints and leads to joint deformity and disability. While conventional treatments for RA include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), natural supplements have been increasingly popular for RA management due to their potential benefits and fewer side effects.
According to a study by CC Rosenbaum et al. (2010), omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements, have been shown to reduce joint pain and stiffness in RA patients by decreasing inflammation in the body. Moreover, turmeric, a spice commonly used in Indian cuisine, contains the active ingredient curcumin, which has been shown to reduce joint inflammation and pain as well.
Another natural supplement suggested for RA management is ginger, which has anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit RA patients. Additionally, vitamin D, either from sunlight or supplements, has been shown to improve bone health in RA patients, who are at a higher risk of osteoporosis due to their condition and treatment. While these natural supplements have shown potential benefits for RA management, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking them as they may interact with other medications or have adverse effects on certain individuals.
The increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity has become a major public health concern worldwide. A sedentary lifestyle and an unhealthy diet have been identified as the major contributors to this epidemic. A study conducted by Cano-Marquina et al. (2013) explored the potential benefits of consuming green tea for weight loss and weight maintenance.
The study found that green tea consumption can increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation, leading to weight loss. Moreover, the catechins present in green tea can reduce body weight and body fat by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fat and enhancing thermogenesis. In addition, green tea consumption has been associated with a decrease in waist circumference, indicating a decrease in abdominal fat. The study also found that green tea can improve lipid and glucose metabolism, which are important for the prevention of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Thus, incorporating green tea into the diet can be a simple and effective way to promote weight loss and weight maintenance while improving overall health.
In conclusion, managing rheumatoid arthritis can be a challenging task, but the use of supplements can help to alleviate the symptoms and improve overall health. The best supplements for rheumatoid arthritis mentioned in this article, including omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and ginger, have proven to be effective in relieving joint pain, inflammation and stiffness.
It is important to remember that while these supplements have shown promising results, they should not replace prescribed medication, and it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before adding any supplements to your diet. By incorporating these supplements into a healthy lifestyle and working with a healthcare team, it is possible to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Rheumatoid Arthritis FAQRheumatoid Arthritis FAQ
What supplements work for rheumatoid arthritis?
There are several supplements that may help manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms, including:
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Green tea
- Vitamin D
- Probiotics
What vitamin is best for rheumatoid arthritis?
Vitamin D is often recommended for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. It helps regulate the immune system and may reduce inflammation.
How to treat artritis reumatoide?
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and therapies. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Can vitamin D reverse rheumatoid arthritis?
Vitamin D alone cannot reverse rheumatoid arthritis, but it may help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options.
Is B12 good for rheumatoid arthritis?
While vitamin B12 plays a role in overall health, there is limited evidence to suggest that it specifically benefits rheumatoid arthritis. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for individualized guidance.
Which vitamin is not good for rheumatoid arthritis?
There is no specific vitamin known to be detrimental to individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. However, excessive doses of certain vitamins may have adverse effects. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate supplementation.
Is there a natural way to fight rheumatoid arthritis?
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, certain lifestyle changes and natural remedies may help manage symptoms. These include regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress reduction techniques, and the use of certain supplements. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Is magnesium good for rheumatoid arthritis?
Magnesium may have some benefits for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. It helps with muscle and nerve function and may aid in reducing pain and inflammation. However, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.